Reading and Writing Files
Storing information in
a file and retrieving it later are useful tasks in any computer program. In
this tutorial you’ll lean to use java.io.File class to accomplish the above
tasks.
Creating
a file in your hard Drive
In
the following example we create an empty file in the directory call “iotest” in
your “C:” drive using mkdir() and createNewFile() method.
package lk.ray.createfile;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class createFile {
public static void
main(String[] args) {
String pathName =
"c:" + File.separator + "iotest";
String fileName =
"c:" + File.separator + "iotest" + File.separator +
"test.txt";
File cD = new
File(pathName);
File cF = new
File(fileName);
try {
cD.mkdir(); //creates the dirctory c:\iotest
cF.createNewFile();//creates
the file test.txt
System.out.println("Created " + cF.getPath());
} catch (IOException e)
{
System.out.println("Could not create the file " +
cF.getPath());
}
}
}
|
Output
Deleting
a file in your hard Drive
Following
program uses the delete() method to delete the test.doc that you have just
created in your “c:\iotest” directory. Exists() method enables you to check
whether the file exists in your hard drive before deletion.
package lk.ray.deletefile;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class deleteFile {
public
static void main(String[] arg) throws IOException {
String file = "D:" + File.separator + "iotest" +
File.separator + "test.txt";
File deleteF = new File(file);
if
(deleteF.exists()) {
deleteF.delete();
System.out.println("Deleted");
}
else {
throw new IOException("File not found");
}
}
}
|
Reading
Content
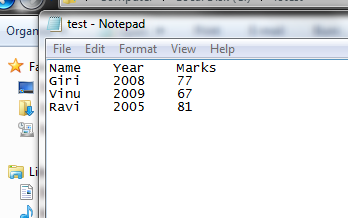
Before
we read from the file, we need to fill some content in to the text file that we
created. Therefore open the temp.txt
file and type some data into three columns.
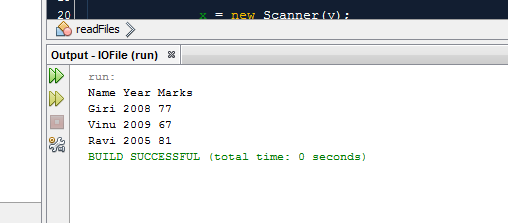
Now
we use Scanner Object to read the content from text file.
package lk.ray.readfile;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class readFiles {
private Scanner x;
public void openFile() {
File y;
y = new File("c:" + File.separator + "iotest" +
File.separator + "test.txt");
try {
x = new Scanner(y);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("Error
" + e.getMessage());
}
}
public void readFile() {
while (x.hasNext()) {
String strA = x.next();
String strB = x.next();
String strC = x.next();
System.out.printf("%s %s
%s\n", strA, strB,strC);
}
}
public void closeFile() {
x.close();
}
public static void main(String[] arg) {
readFiles rF = new readFiles();
rF.openFile();
rF.readFile();
rF.closeFile();
}
}
|
Output